OVERVIEW
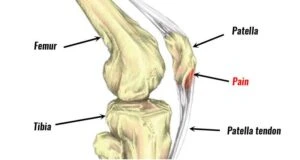
Patellar Tendinitis (Jumper’s Knee)
Jumping sports like basketball and volleyball put a lot of strain on the kneecaps and attached tendons. Patellar tendonitis symptoms include tenderness to the patellar tendon, and sometimes swelling. Physical therapy and activity modification are some of the options for treatment.
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson is a specific disorder of the patellar tendon where it attaches to the base of the kneecap. Osgood-Schlatter is an Osgood-Schlatter disorder, which affects the tendon at the tibial tubrosity of the leg. Both of these disorders are common in mature teens. The treatment options include activity modification, physical therapy, or, rarely, surgical excision of necrotic debris.
TREATMENT
Possible Treatments
- Aerobic/Endurance Exercise
- Core Strengthening
- Cryotherapy or Cold Therapy
- Electrotherapeutic Modalities
- Gait or Walking Training
- Iontophoresis
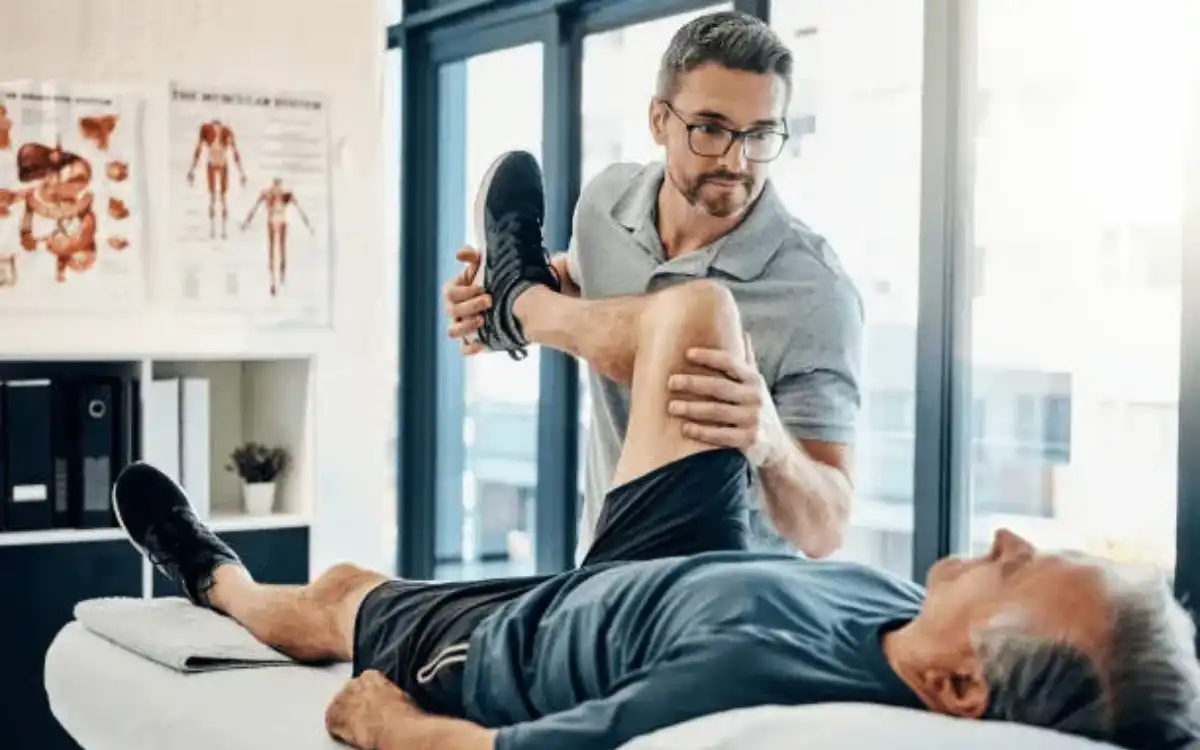
- Knee Active Range of Motion
- Knee Joint Mobilization
- Knee Passive Range of Motion
- Knee Resistive Range of Motion
- Plyometrics
- Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF)
- Proprioception Exercises
- Physical Agents
- Soft Tissue Mobilization
- Stretching/Flexibility Exercise
GOALS
Possible Treatment Goals
- Improve Balance
- Decrease Risk of Reoccurrence
- Improve Fitness
- Improve Function
- Improve Muscle Strength and Power
- Increase Oxygen to Tissues
- Improve Proprioception
- Improve Range of Motion
- Self-care of Symptoms
- Improve Tolerance for Prolonged Activities