OVERVIEW
Sprains and Strains:
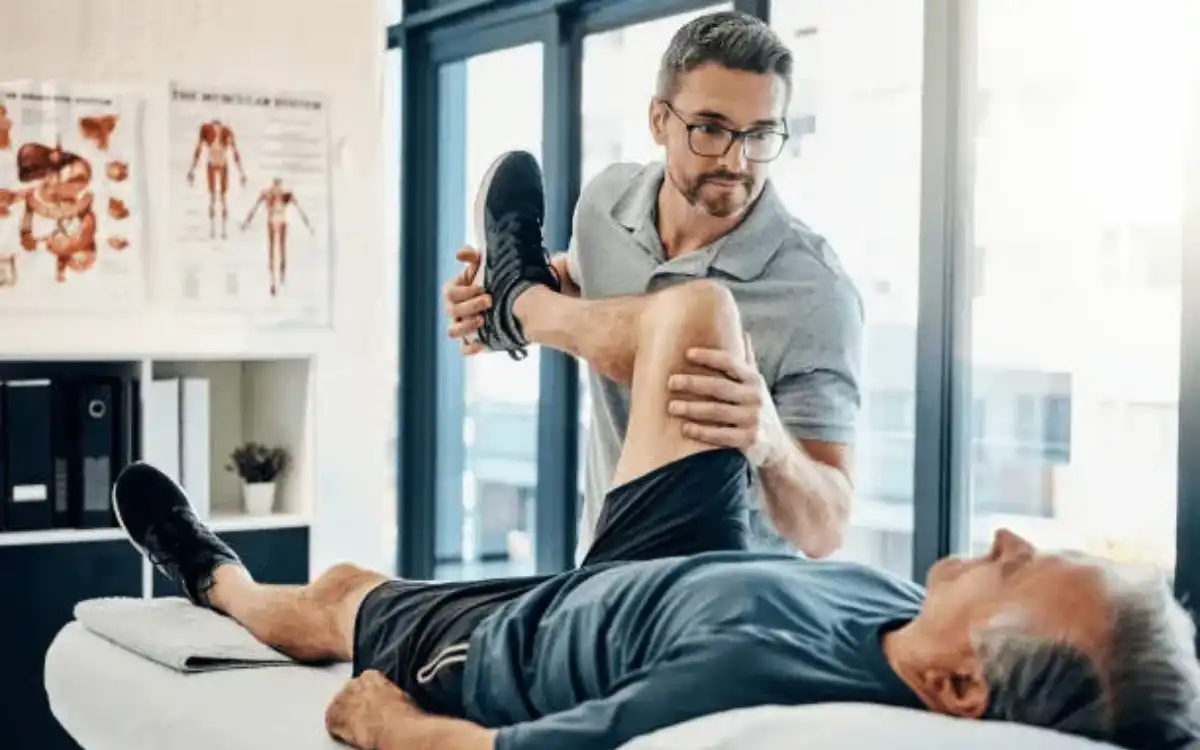
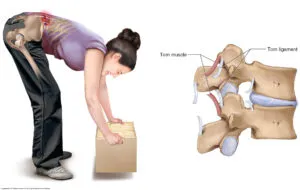
Sprains and strains can be common injuries in daily life, as well as during recreation and competitive sports. What is a sprain?
Strains
A strain is when muscle fibers are torn. Your muscles are made up of individual muscle fibers. A strain occurs when you force a muscle to contract repeatedly or in a strong way. The grades I to III are used to classify strains. These grades can also be referred to as mild ( Grade I), medium ( Grade II), and severe ( Grade III).
A Grade I strain refers to a slight disruption of muscle fibers. Mild swelling and tenderness may occur. It may also be difficult to stretch the muscle and use it.
A grade II muscle strain indicates moderate muscle fiber damage. It may cause moderate to severe pain, it can be difficult to stretch and use the injured muscle, and it could also lead to ecchymosis. Commonly known as bruising, ecchymosis is a sign that there has been internal bleeding. The bleeding can often be seen under the skin in the form of a purple or blue color, red, yellow, or even green.
The most severe grade 3 strain is. This is when a muscle is torn into two or more pieces. It can cause severe pain and complete loss of muscle strength. There may also be swelling, ecchymosis, or a “indentation” in the area where the muscle has been torn. Medical intervention is often necessary. An orthopaedist, a musculoskeletal specialist, will typically evaluate your condition. If necessary, he or she may recommend surgical repair.
Sprains
Sprains refer to tears in the ligaments or capsules (tissues surrounding joints). Ligaments are composed of bundles of collagen tissue that is elastic and connects one bone to the next. The capsules surround the joint in a partial or complete manner. The synovial fluid, which is the lubricating and nurturing fluid that surrounds a joint, is found in the capsule.
Sprains can be classified in grades I, II or III according to their severity.
A grade 1 sprain is a sprain that involves very few ligament fibers. You may feel some pain or swelling.
A grade 2 sprain refers to a partial or moderate ligament tear. A grade II ligament sprain is one that causes moderate to severe pain. There may be swelling, bruising, and joint dysfunction (e.g., difficulty or inability to walk due to the severity of the injury).
A grade 3sprain refers to a complete tear of the joint capsule or ligament. A grade III sprain can cause severe pain, swelling, bruising and loss of function. As with grade III strains, orthopaedic intervention/surgical repair may be necessary.
In sports like football, rugby and soccer, hip pointers can be caused by a direct blow at the iliac crown. Pain, swelling, and tenderness around the bony prominence on the hip side can be signs and symptoms. The treatment is usually rest, ice and compression.
TREATMENT
GOALS
Possible Treatment Goals
- Improve Balance
- Decrease Risk of Reoccurrence
- Improve Fitness
- Improve Function
- Improve Muscle Strength and Power
- Increase Oxygen to Tissues
- Improve Proprioception
- Improve Range of Motion
- Improve Relaxation
- Self-care of Symptoms
- Improve Safety
- Improve Tolerance for Prolonged Activities
- Improve Wound Healing